Miscellaneous Tools¶
timvis scripts¶
Scripts timvis.gmt and timvis_abs.gmt are used to visualize the elapsed time of the
computation obtained with the input parameter stopwatch_mode = .true.
by using GMT versions 5 or later.
Geographic Coordinate Conversion¶
The Fortran programs ll2xy.x and xy2ll.x can project and inversely
project the geographic and Cartesian coordinates with the same algorithm
as OpenSWPC. These tools are provided for OpenSWPC version 3.0 or
later.
wvconv.x: a waveform conversion tool from 2D to 3D¶
New in version 5.2
is a tool to convert 2D simulation results into 3D-simulation-equivalent seismic waveforms.
Let us denote the 3D seismic waveform from a point source located at as . The 2D simulation result from a point source at can be expressed by line integral with respect to y-direction as
The inverse transformation can be written as 1
where is a propagation distance, and is a seismic velocity at each phase appeared in the waveform. The simbol denotes convolution integral.
The tool wvconv.x evaluate this translation by frequency-domain calculation with assumptions that and are both constant:
In the calculation, is assuumed to be a straight line between the source and the receiver. The value of can be given as a parameter, but by default it is calculated assuming m/s.
Usage:¶
1 2 3 4 | |
As an example, the following figure shows a comparison between the waveform calculated with the P-SV 2D code in the 1D structure of example/lhm.dat and converted by wvconv.x ( m/s) and the result of 3D calculation with the same structure.
Figure
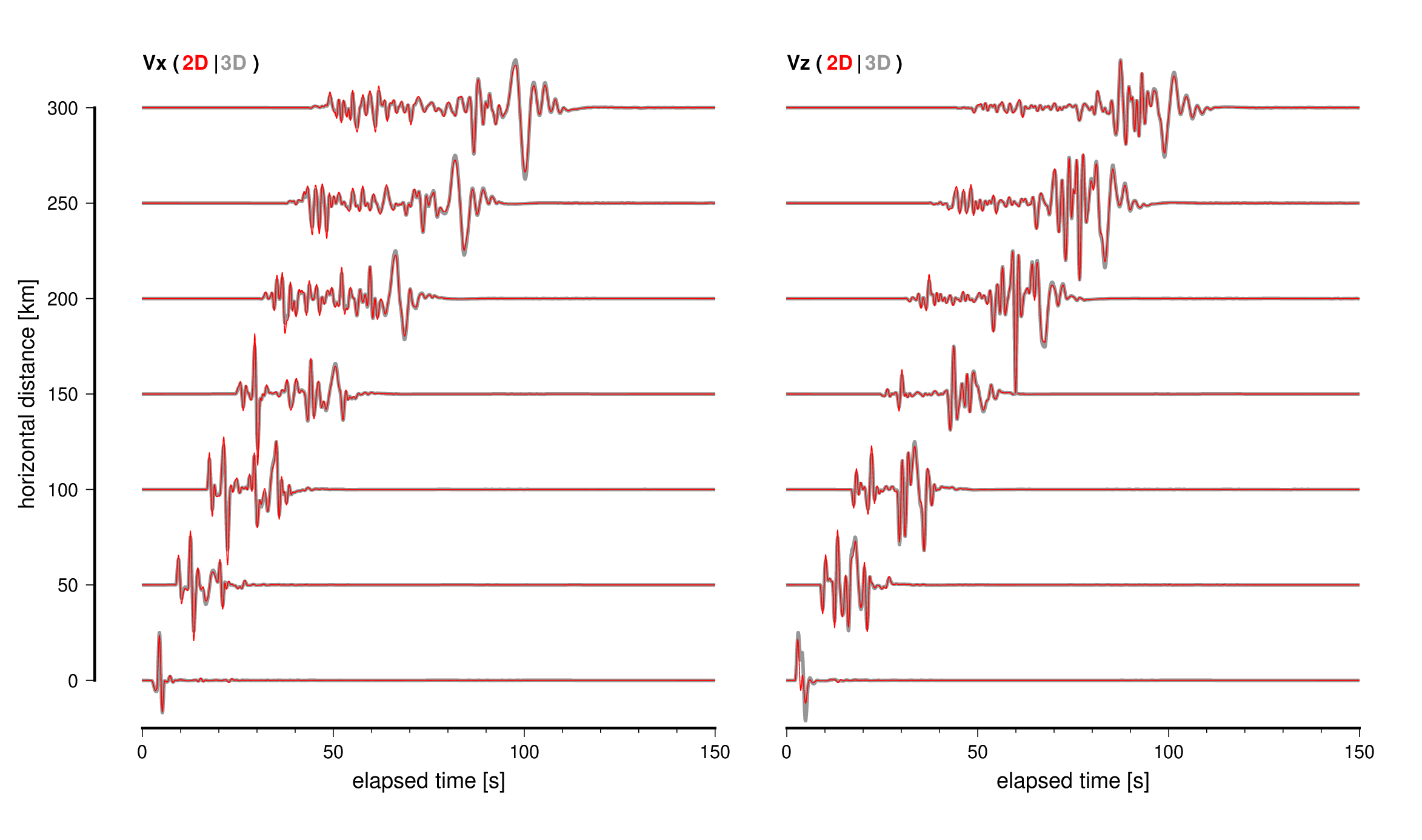 Comparison of 3D simulation results (gray curve) and 2D P-SV simulation results converted by
Comparison of 3D simulation results (gray curve) and 2D P-SV simulation results converted by wvconv.x (red curve).
Since the velocity of the seismic phase is assumed to be 4000 m/s, the amplitudes of the P-wave and subsequent surface wave phases are slightly different, but in general, the waveforms are in very good agreement. If the comparison is made without wvconv.x, the amplitudes and shapes of the waveforms are completely different.
Warning
wvconv.x is a very new code introduced in Version 5.2, and might contain bug(s). Please use it with caution.
-
Li, D., Helmberger, D., Clayton, R. W., & Sun, D. (2014). Global synthetic seismograms using a 2-D finite-difference method. Geophysical Journal International, 197(2), 1166–1183. doi:10.1093/gji/ggu050 ↩